- Home
- About us
-
Products
 The first developed technology platform with various application scenarios, including infectious disease, fertility, DOA, etc.
The first developed technology platform with various application scenarios, including infectious disease, fertility, DOA, etc. 50+ kinds of reagents and five high-performance devices, focusing on detecting cardiovascular disease, inflammation, kidney injury, sex hormones, thyroid function, diabetes, tumor, and others.
50+ kinds of reagents and five high-performance devices, focusing on detecting cardiovascular disease, inflammation, kidney injury, sex hormones, thyroid function, diabetes, tumor, and others. Single-dose Chemiluminescense Immunoassay Platform
Single-dose Chemiluminescense Immunoassay Platform Wondfo optical blood coagulation analyzer is the first one in the world that can test PT, APTT, TT, FIB, and ACT simultaneously.
Wondfo optical blood coagulation analyzer is the first one in the world that can test PT, APTT, TT, FIB, and ACT simultaneously. Our Blood Gas Analyzer BGA-102 can produce the result in 30s. Its advantages of portability, easy operation, durability, and high performance make it ideal for clinics, laboratories, and hospitals.
Our Blood Gas Analyzer BGA-102 can produce the result in 30s. Its advantages of portability, easy operation, durability, and high performance make it ideal for clinics, laboratories, and hospitals. Ready-to-use lyophilized RT-PCR Reagent;
Ready-to-use lyophilized RT-PCR Reagent;
Gold Standard for COVID-19 Diagnosis Wondfo PA-3600 IHC Staining System
Wondfo PA-3600 IHC Staining System The Wondfo Truth-H80E HPLC Hemoglobin Analyzer is a high-performance diagnostic device designed for rapid and precise measurement of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)—the gold standard for diabetes diagnosis.It support the standard mode and variant mode and provide the result within 60-90seconds.
The Wondfo Truth-H80E HPLC Hemoglobin Analyzer is a high-performance diagnostic device designed for rapid and precise measurement of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)—the gold standard for diabetes diagnosis.It support the standard mode and variant mode and provide the result within 60-90seconds. -
Solutions
 This year, the summit will place a special focus on collaboration across different fields to explore the application of POCT and optimize clinical pathways. In the meantime, drive innovation by adoption of new technologies and biomarkers.
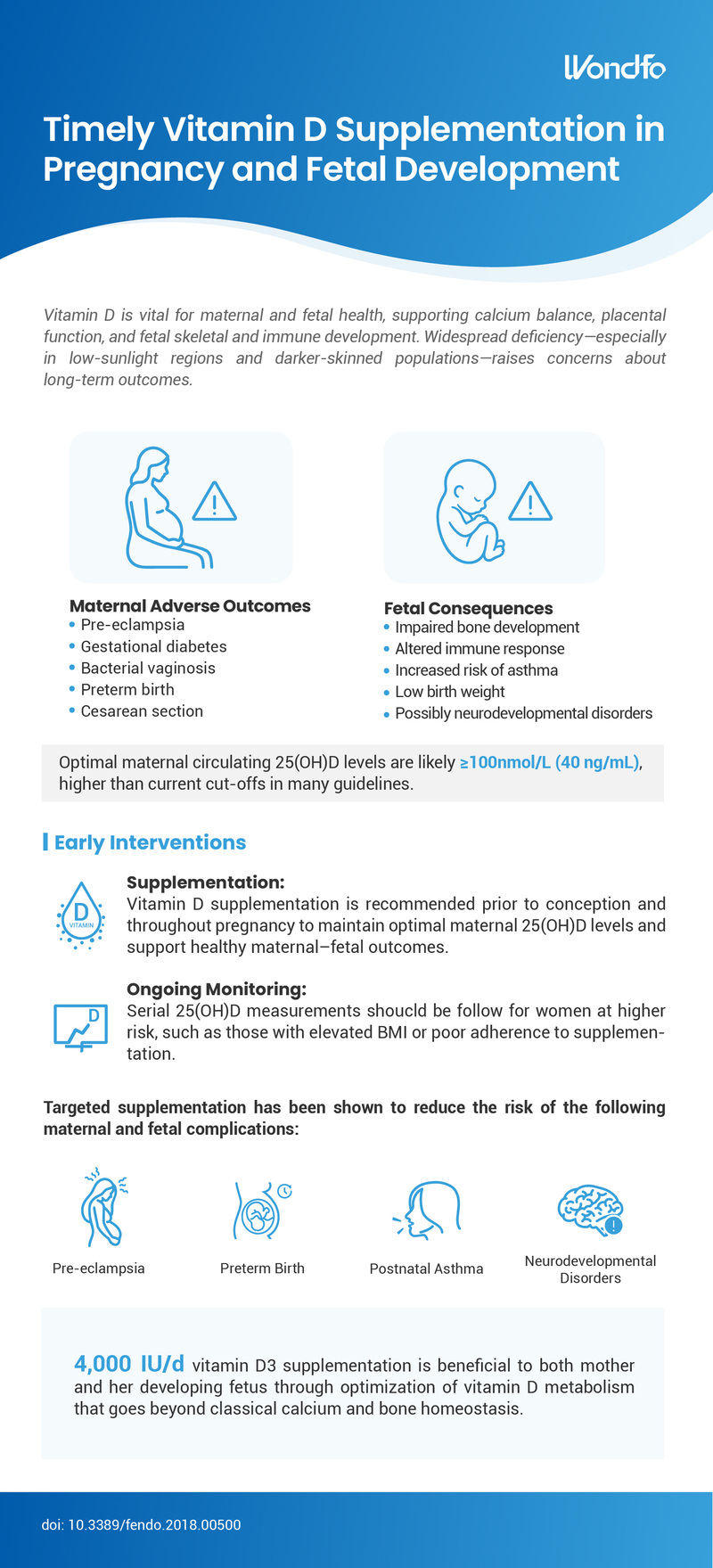
This year, the summit will place a special focus on collaboration across different fields to explore the application of POCT and optimize clinical pathways. In the meantime, drive innovation by adoption of new technologies and biomarkers.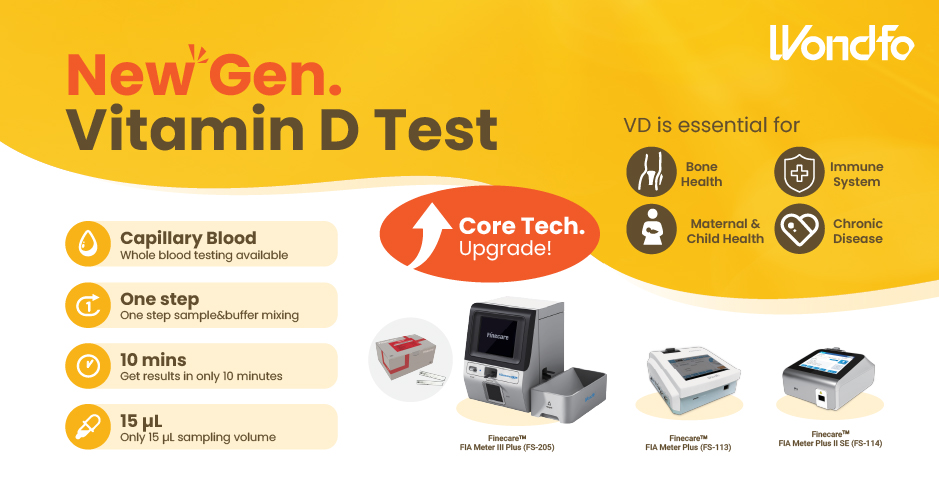 Finecare™ Vitamin D, from complexity to simplicity
Finecare™ Vitamin D, from complexity to simplicity Building A World Free from Antibitoic Overuse
Building A World Free from Antibitoic Overuse Advanced rapid diagnostic test with WHO prequalification for infectious disease
Advanced rapid diagnostic test with WHO prequalification for infectious disease The Future Intelligent Medical Assistant to Healthcare
The Future Intelligent Medical Assistant to Healthcare Fight against the pandemic through continuous innovation
Fight against the pandemic through continuous innovation - Careers
- Resource Center
- News & Press
- Contact Us