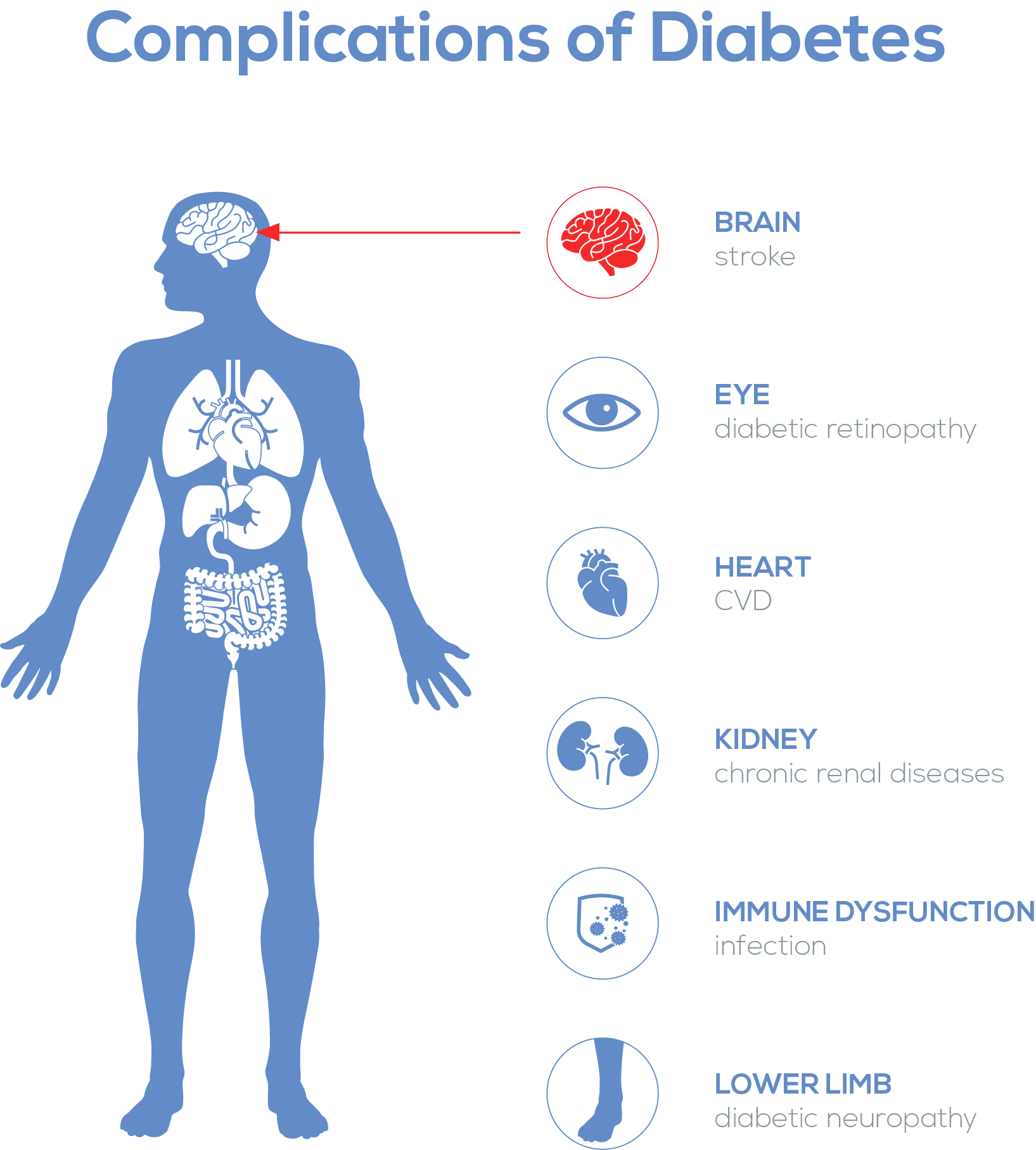
The prevalence of diabetes has quadrupled from 1980 to 2014 according to WHO. According to researches by the International Diabetes Federation, 537 million adults globally are living with diabetes, and about 4/5 of them are left undiagnosed. Frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger…Symptoms of diabetes seem not as terrifying as heart attack or hypertension, but its complications can be highly torturing. High blood glucose can damage all vessels in human body, causing complications in multiple organs, such as blindness due to diabetic retinopathy and lower limb amputation because of diabetic neuropathy. Furthermore, high blood glucose level can trigger immune dysfunction, so people with diabetes are more susceptible to infection, for example, slow healing of wounds.
Tests for Diabetes
Blood Sugar Tests: For people diagnosed with diabetes, frequent test of glucose level is required. It detects the instant sugar level in your blood, helping proper diet decisions. But the test result may be affected by when and what you eat lately, so continuous monitoring and recording are needed for impaired judgement. The result of blood sugar test with fingerstick blood sample cannot be an evidence for diabetes diagnosis. What’s more, the glucose level can also alter at acute infection and trauma, and glucose level then is not valid for diagnosis.
HbA1c Test: After what we eat has been digested and converted into sugar in blood, the concentration of blood sugar rises. The hemoglobin in blood cell combines sugar and becomes glycated hemoglobin. This reaction is considerably slow and the level of glycated hemoglobin is seldom affected. Glycated hemoglobin can be categorized into 3 kinds: HbA1a, HbA1b and HbA1c, and HbA1c contributes to 70% of glycated hemoglobin. Therefore, HbA1c can generally reflect the average level of blood sugar over the past 2 to 3 months and is used for diabetes diagnosis and long-term monitoring. People who have diabetes need this test regularly, and result of A1c test also detect prediabetes, assisting early management.
How to Test HbA1c
The hemoglobin A1c test requires a sample of blood. If the test is performed at a lab, the sample is taken through a needle from a vein. If the test is performed in a doctor’s office or taken at home, a finger-prick is used to obtain the blood sample. As the HbA1c level reflects the average blood sugar level in last several months and is not affected by recent eating, fasting is not required before testing.
What’s the Meaning of the HbA1c Test Result?
According to the report “Use of Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) in the Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus” from World Health Organization, HbA1c can be used as a diagnostic test for diabetes. HbA1c of 6.5% is recommended as the cut point for diagnosing diabetes by WHO. If your HbA1c test result is over the threshold, you need to consult your general practitioner for further advice.
Point-of-care HbA1c Test
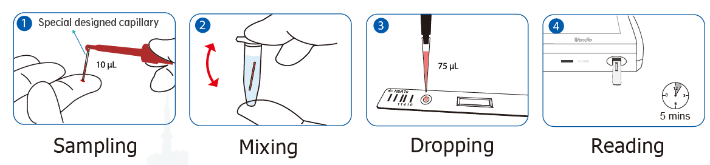
HbA1c test can be done with traditional analyzers installed in labs, but as medical technology improves, point-of-care test for HbA1c have been developed. Point-of-care testing (POCT) is defined as medical diagnostic testing at or near the point of care—that is, at the time and place of patient care. POCT provides immediate results on spot of patient consultation to enable diagnosis and treatment as early as possible.
POCT HbA1c test is usually employed with portable instruments, making it possible to be used in various scenarios, such as doctor’s office, mobile team providing healthcare, pharmacy, or even at home as self-test.
To ensure convenience and patient’s satisfaction, blood sample for POCT HbA1c test is usually collected with finger-prick and results can be released within several minutes.
There is some evidence supporting the use of POCT for HbA1c analysis: studies report in the primary care shows that POCT-A1c device used in the primary care unit is a cost-effective alternative, which improves access to A1c tests and results in an increased rate of early control of blood glucose.
Wondfo HbA1c Rapid Quantitative Test is applied on portable Finecare analyzer with simple operations, and results can be delivered in 5 minutes. This CE-marked test is certified by NGSP and IFCC, and has been distributed to more than 50 countries in the last five years.
Wondfo
Racing For Life
Since 1992, Wondfo has focused all efforts on the R&D, production, sales, and improvement of its leading POCT solutions. We promise to provide people worldwide with life-changing technology to ensure everybody's health and happiness.
 The first developed technology platform with various application scenarios, including infectious disease, fertility, DOA, etc.
The first developed technology platform with various application scenarios, including infectious disease, fertility, DOA, etc. 50+ kinds of reagents and five high-performance devices, focusing on detecting cardiovascular disease, inflammation, kidney injury, sex hormones, thyroid function, diabetes, tumor, and others.
50+ kinds of reagents and five high-performance devices, focusing on detecting cardiovascular disease, inflammation, kidney injury, sex hormones, thyroid function, diabetes, tumor, and others. Single-dose Chemiluminescense Immunoassay Platform
Single-dose Chemiluminescense Immunoassay Platform Wondfo optical blood coagulation analyzer is the first one in the world that can test PT, APTT, TT, FIB, and ACT simultaneously.
Wondfo optical blood coagulation analyzer is the first one in the world that can test PT, APTT, TT, FIB, and ACT simultaneously. Our Blood Gas Analyzer BGA-102 can produce the result in 30s. Its advantages of portability, easy operation, durability, and high performance make it ideal for clinics, laboratories, and hospitals.
Our Blood Gas Analyzer BGA-102 can produce the result in 30s. Its advantages of portability, easy operation, durability, and high performance make it ideal for clinics, laboratories, and hospitals. Ready-to-use lyophilized RT-PCR Reagent;
Ready-to-use lyophilized RT-PCR Reagent; Wondfo PA-3600 IHC Staining System
Wondfo PA-3600 IHC Staining System The Wondfo Truth-H80E HPLC Hemoglobin Analyzer is a high-performance diagnostic device designed for rapid and precise measurement of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)—the gold standard for diabetes diagnosis.It support the standard mode and variant mode and provide the result within 60-90seconds.
The Wondfo Truth-H80E HPLC Hemoglobin Analyzer is a high-performance diagnostic device designed for rapid and precise measurement of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)—the gold standard for diabetes diagnosis.It support the standard mode and variant mode and provide the result within 60-90seconds. This year, the summit will place a special focus on collaboration across different fields to explore the application of POCT and optimize clinical pathways. In the meantime, drive innovation by adoption of new technologies and biomarkers.
This year, the summit will place a special focus on collaboration across different fields to explore the application of POCT and optimize clinical pathways. In the meantime, drive innovation by adoption of new technologies and biomarkers. Finecare™ Vitamin D, from complexity to simplicity
Finecare™ Vitamin D, from complexity to simplicity Building A World Free from Antibitoic Overuse
Building A World Free from Antibitoic Overuse Advanced rapid diagnostic test with WHO prequalification for infectious disease
Advanced rapid diagnostic test with WHO prequalification for infectious disease The Future Intelligent Medical Assistant to Healthcare
The Future Intelligent Medical Assistant to Healthcare Fight against the pandemic through continuous innovation
Fight against the pandemic through continuous innovation